Clinical Dermatology
Infections & Skin Diseases: Diagnosis and Targeted Treatment
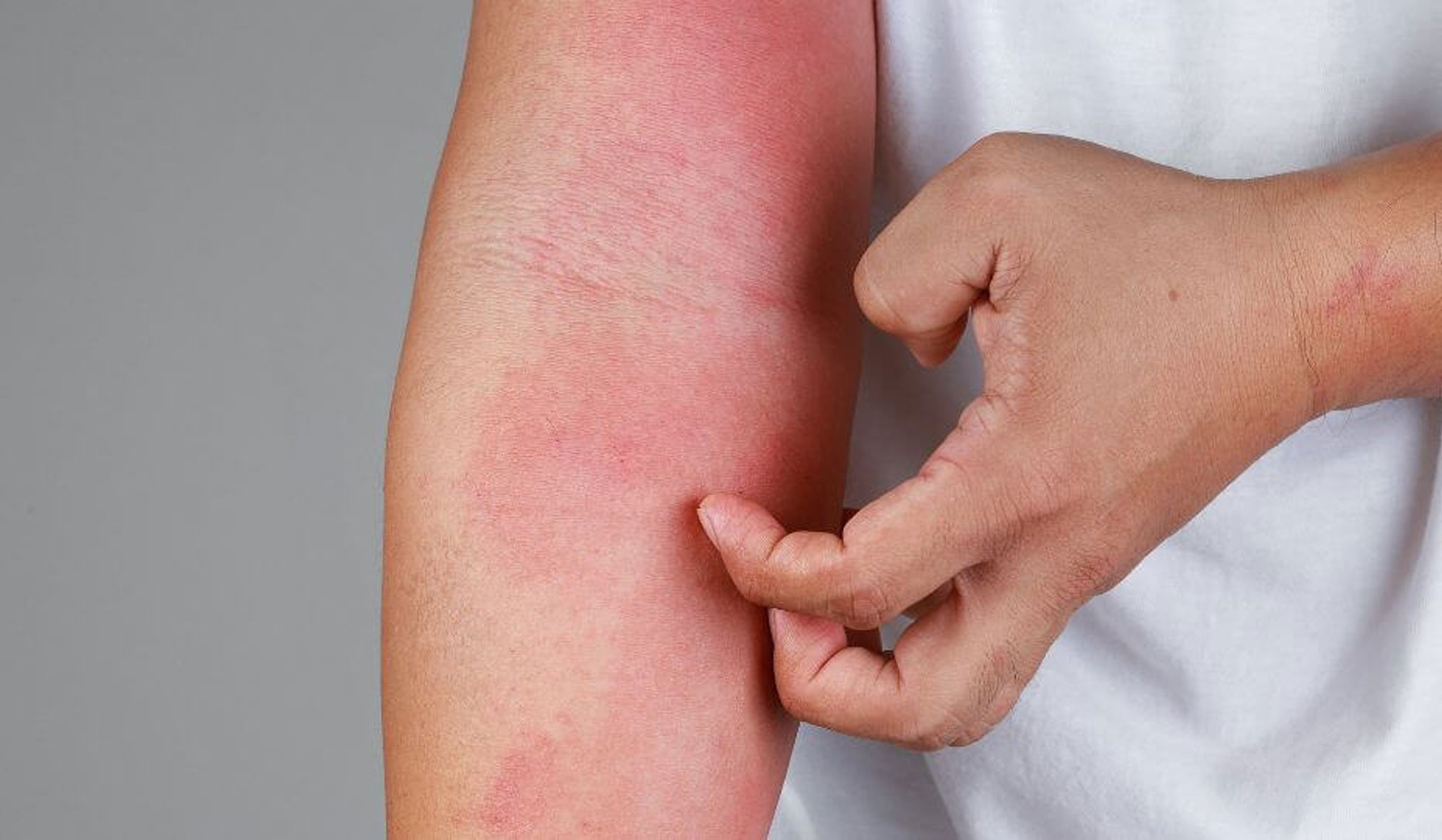
Your skin is your body’s first line of defense. When infections strike, timely and accurate diagnosis followed by the right treatment is essential for rapid recovery and prevention of complications. We specialize in the comprehensive care of fungal, bacterial, and viral skin infections using evidence-based protocols and advanced diagnostics.
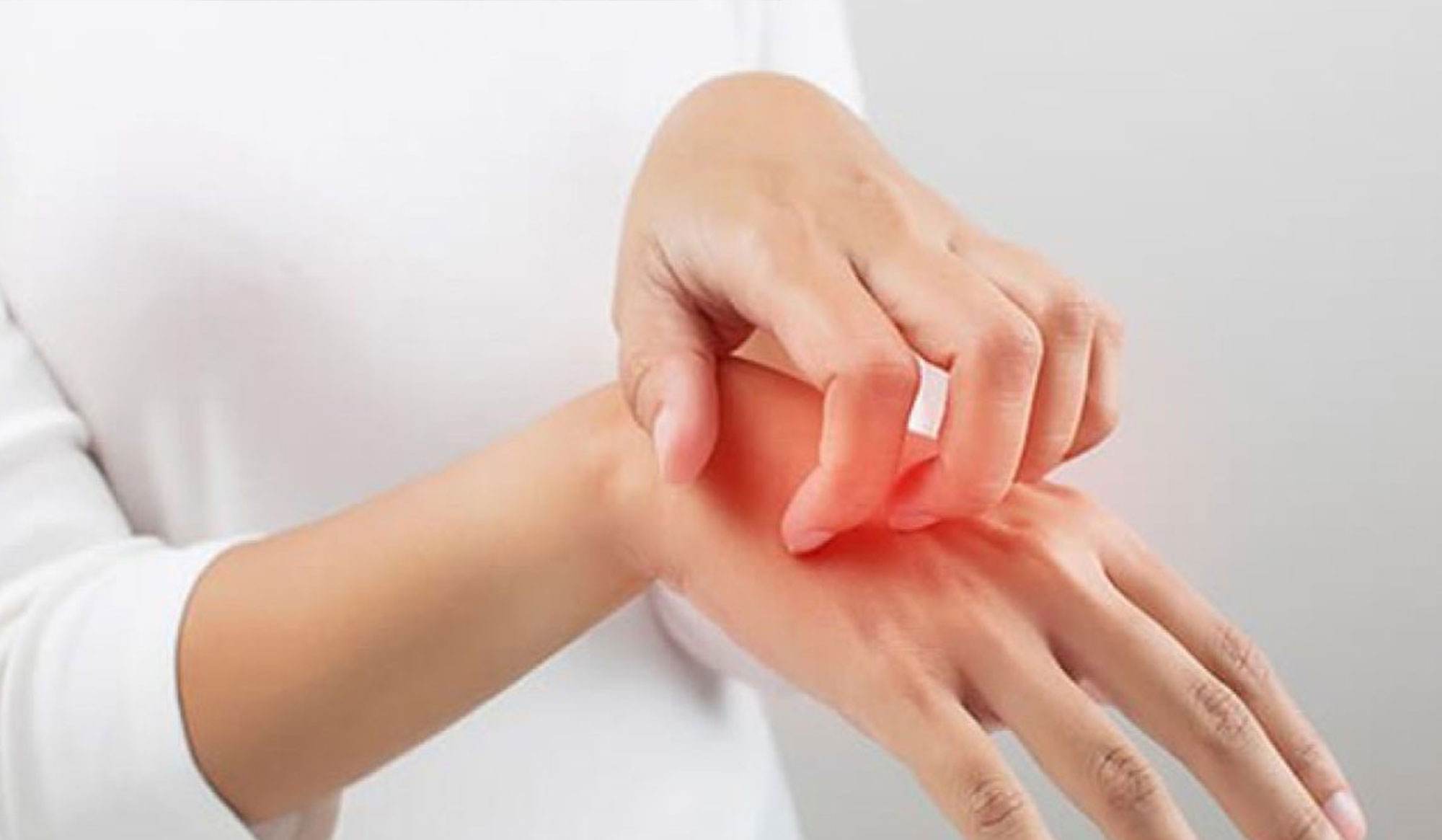
Common Skin Infections We Treat
1. Fungal Infections
- Types:
- Tinea (ringworm, athlete’s foot, jock itch, scalp infection)
- Candidiasis (yeast infection of skin folds, nails, mouth)
- Symptoms:
- Redness, itching, peeling, scaling, circular rashes, soreness in moist areas.
- Diagnosis:
- Clinical examination
- KOH prep, fungal cultures, dermoscopy
- Treatment:
- Topical or oral antifungal medications
- Skin barrier repair and hygiene advice
2. Bacterial Infections
- Types:
- Impetigo (highly contagious, often in children)
- Cellulitis, folliculitis, boils
- Symptoms:
- Pus-filled lesions, crusting, redness, swelling, fever (in severe cases)
- Diagnosis:
- Visual inspection
- Swab cultures for antibiotic sensitivity
- Blood tests (if systemic signs)
- Treatment:
- Topical or oral antibiotics
- Proper wound care and hygiene education
3. Viral Infections
- Types:
- Herpes Simplex (cold sores, genital herpes)
- Molluscum Contagiosum (common in children and immunocompromised adults)
- Warts (caused by HPV)
- Symptoms:
- Painful blisters, grouped vesicles (herpes), pearly papules (molluscum), rough bumps (warts)
- Diagnosis:
- Clinical signs
- Tzanck smear, PCR tests, dermoscopy
- Treatment:
- Antiviral creams or tablets
- Cryotherapy, laser therapy for molluscum and warts
- Recurrence prevention and immune support
Our Diagnostic Approach
We believe in precision medicine:
- Dermatologist consultation with clinical evaluation
- Skin scrapings/swabs for lab tests
- Microscopy, cultures, PCR, or biopsies as needed
- Custom treatment plans based on type, severity, and recurrence history
Management Protocols
| Infection Type | First-line Treatment | Advanced/Severe Case Management |
|---|---|---|
| Fungal | Topical antifungals (azoles, allylamines) | Oral antifungals, hygiene protocols |
| Bacterial | Topical antibiotics (mupirocin) | Oral antibiotics, abscess drainage |
| Viral | Topical antivirals | Oral antivirals, cryotherapy, immune modulators |
Pros & Cons of Treatments
| Treatment Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Topical medications | Non-invasive, localized treatment | Requires consistent application, slower effect in deeper infections |
| Oral medications | Faster relief, effective for severe infections | Risk of side effects (GI upset, liver function impact) |
| Cryotherapy/Laser | Fast removal of lesions (molluscum, warts) | May cause temporary discomfort, scarring risk |
| Antiviral therapy | Reduces outbreak frequency, speeds healing | Does not cure herpes; long-term use may be needed |
| Culture & Sensitivity Testing | Targeted antibiotic use, avoids resistance | Time-consuming, additional cost |
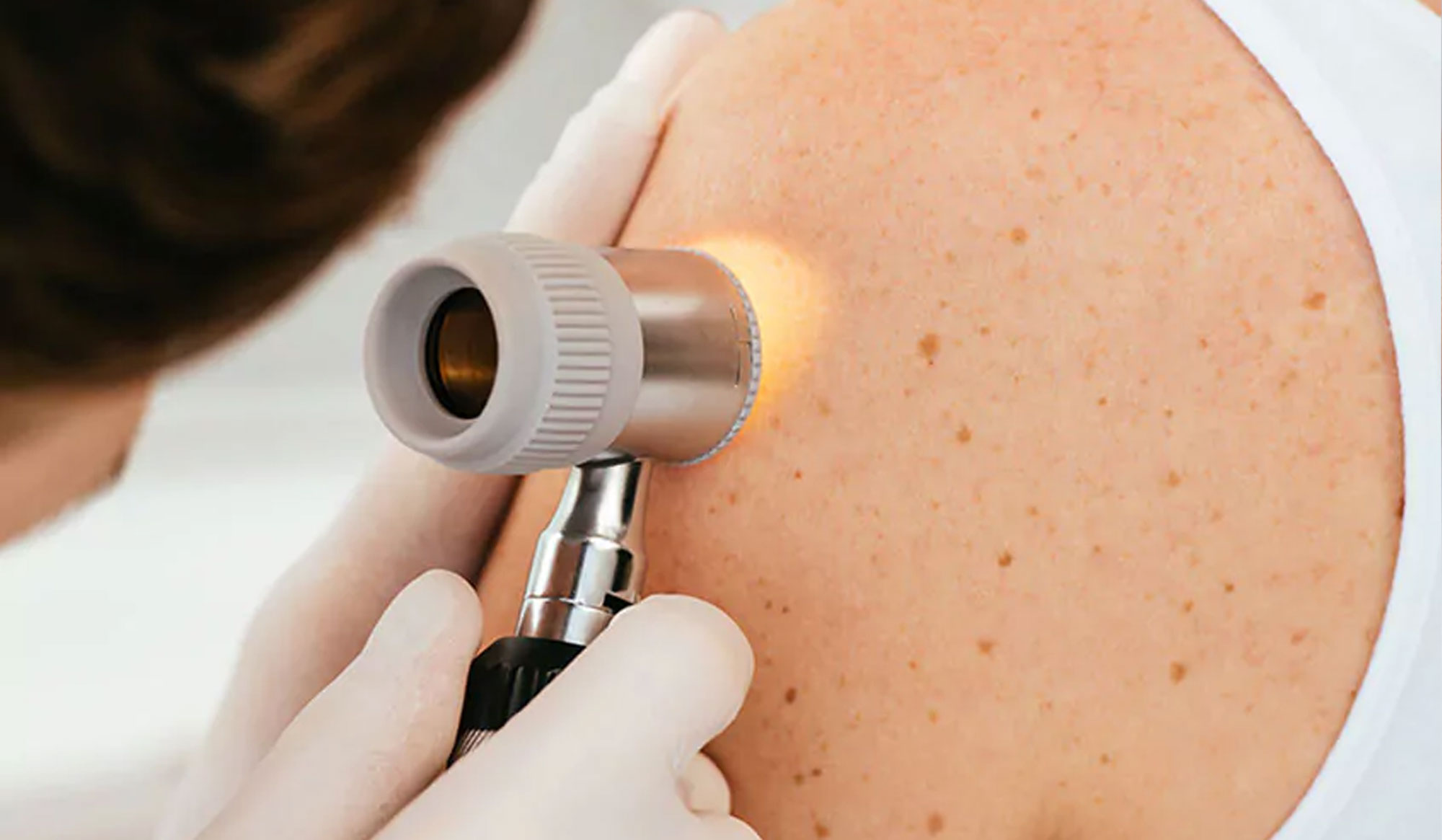
Clinical Dermatology
Allergic & Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Comfort starts with understanding and treating your skin’s sensitivity.
Allergic and inflammatory skin disorders can cause persistent discomfort, itching, and visible irritation affecting both daily life and self-confidence. Our dermatology team offers specialized diagnostic tools and targeted treatment protocols to help patients manage these chronic or recurrent conditions with lasting relief.
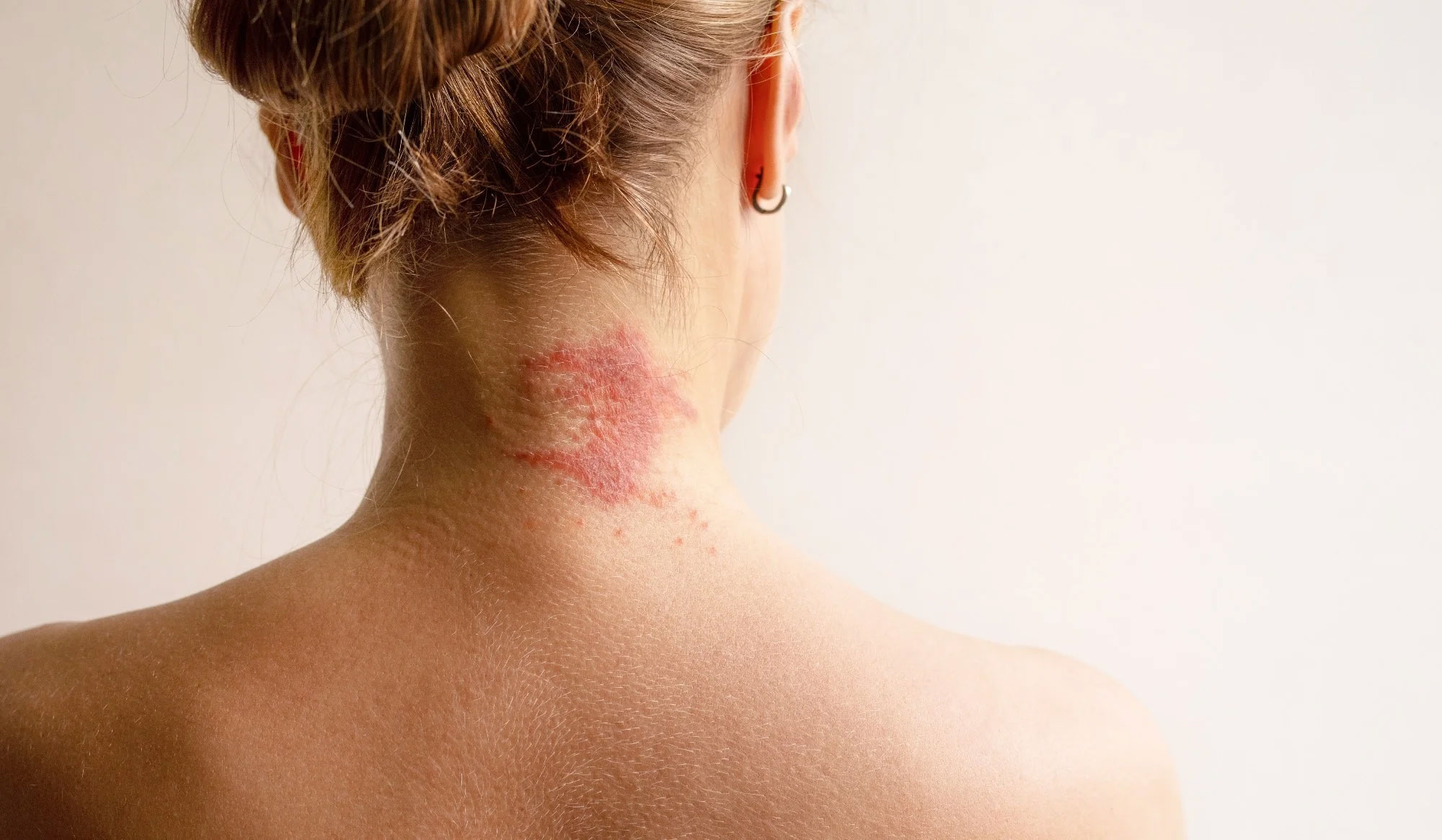

Conditions We Treat
1. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- What it is: A chronic, itchy skin disorder commonly seen in children and adults with a family history of allergies.
- Symptoms: Dryness, redness, intense itching, thickened or cracked skin—often in skin folds, hands, face.
- Management:
- Emollient-rich skincare
- Topical corticosteroids & calcineurin inhibitors
- Allergen avoidance & lifestyle guidance
2. Contact Dermatitis (Irritant & Allergic)
- What it is: Skin inflammation caused by direct exposure to irritants (e.g., soaps) or allergens (e.g., fragrances, metals).
- Symptoms: Red, itchy rashes, sometimes blistering or peeling after contact.
- Diagnosis:
- Patch Testing to identify specific allergens
- Treatment:
- Topical steroids
- Protective barrier creams
- Allergen avoidance strategies
3. Urticaria (Hives)
- What it is: Sudden onset of red, itchy welts due to allergic or autoimmune triggers.
- Types: Acute (short-term) or Chronic (>6 weeks); can be spontaneous or induced (cold, pressure, heat).
- Management:
- Non-sedating antihistamines
- Short courses of oral steroids (in severe flares)
- Immunomodulators for chronic/refractory cases
- Identification of triggers (food, drugs, stress)
Diagnostic Tools
- Patch Testing: Identifies delayed-type allergic reactions to common substances such as metals, dyes, preservatives, and more.
- Blood Tests (e.g., IgE levels for atopic conditions)
- Skin Biopsy (if diagnosis is uncertain)
Treatment Approach
| Condition | First-line Treatment | Advanced/Adjunct Management |
|---|---|---|
| Eczema/Atopic Dermatitis | Moisturizers, topical steroids | Calcineurin inhibitors, phototherapy, immunosuppressants |
| Contact Dermatitis | Allergen avoidance, barrier creams | Patch testing, oral corticosteroids |
| Urticaria | Non-sedating antihistamines | Montelukast, omalizumab (for chronic urticaria) |
Pros & Cons of Treatments
| Treatment Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Topical treatments | Easy to apply, localized effect | May need long-term use; potential steroid side effects |
| Patch Testing | Pinpoints specific allergen causes | Time-consuming; delayed results over 48–72 hrs |
| Oral antihistamines | Fast relief, suitable for hives | May cause drowsiness in some individuals |
| Immunomodulators | Effective for chronic and steroid-resistant cases | Higher cost, needs regular monitoring |
Patient Education & Support
- Customized skincare plans
- Trigger-avoidance strategies
- Allergen awareness & lifestyle counseling
Clinical Dermatology
Hair & Scalp Disorders
Restore your hair. Reclaim your confidence.
Common Conditions We Treat
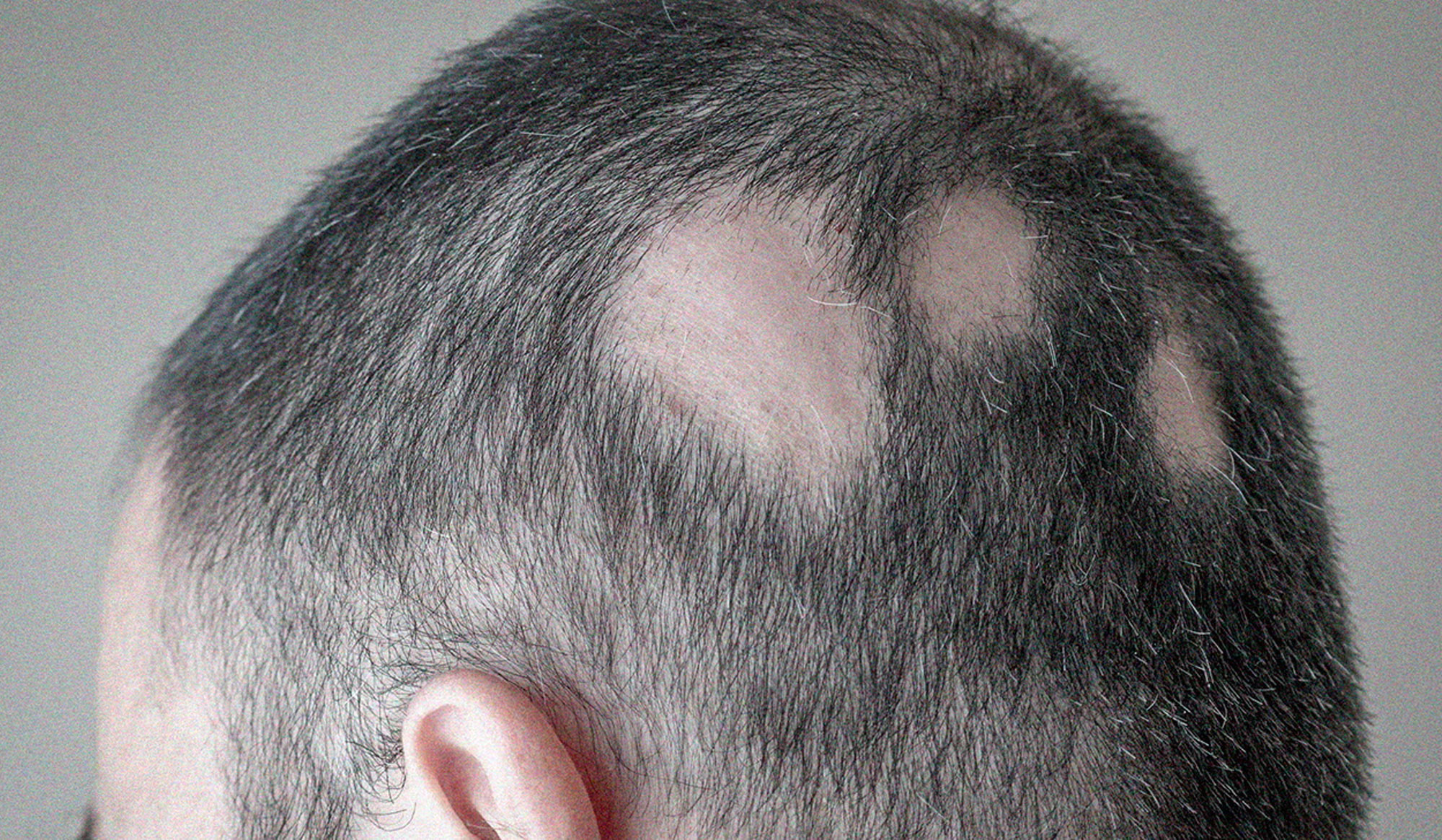
1. Alopecia Areata
- What it is: Autoimmune condition where the body attacks hair follicles, causing patchy hair loss.
- Symptoms: Sudden circular bald spots on the scalp, beard, eyebrows, or other areas.
- Diagnosis:
- Trichoscopy: Shows exclamation mark hairs, yellow dots.
- Blood work (for autoimmune indicators)
- Allergen avoidance & lifestyle guidance
- Treatment:
- Intralesional corticosteroids
- Topical immunotherapy
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
- Psychological counseling (when needed)
2. Androgenetic Alopecia (Male/Female Pattern Baldness)
- What it is: Genetic hair thinning due to hormonal sensitivity of hair follicles.
- Symptoms: Receding hairline in men, diffuse thinning in women (especially crown area).
- Diagnosis:
- Trichoscopy: Miniaturized follicles, variation in hair shaft diameter
- Treatment:
- Minoxidil (topical)
- Finasteride (oral; for men)
- PRP Therapy
- Microneedling & low-level laser therapy
- Hair transplantation (in advanced cases)
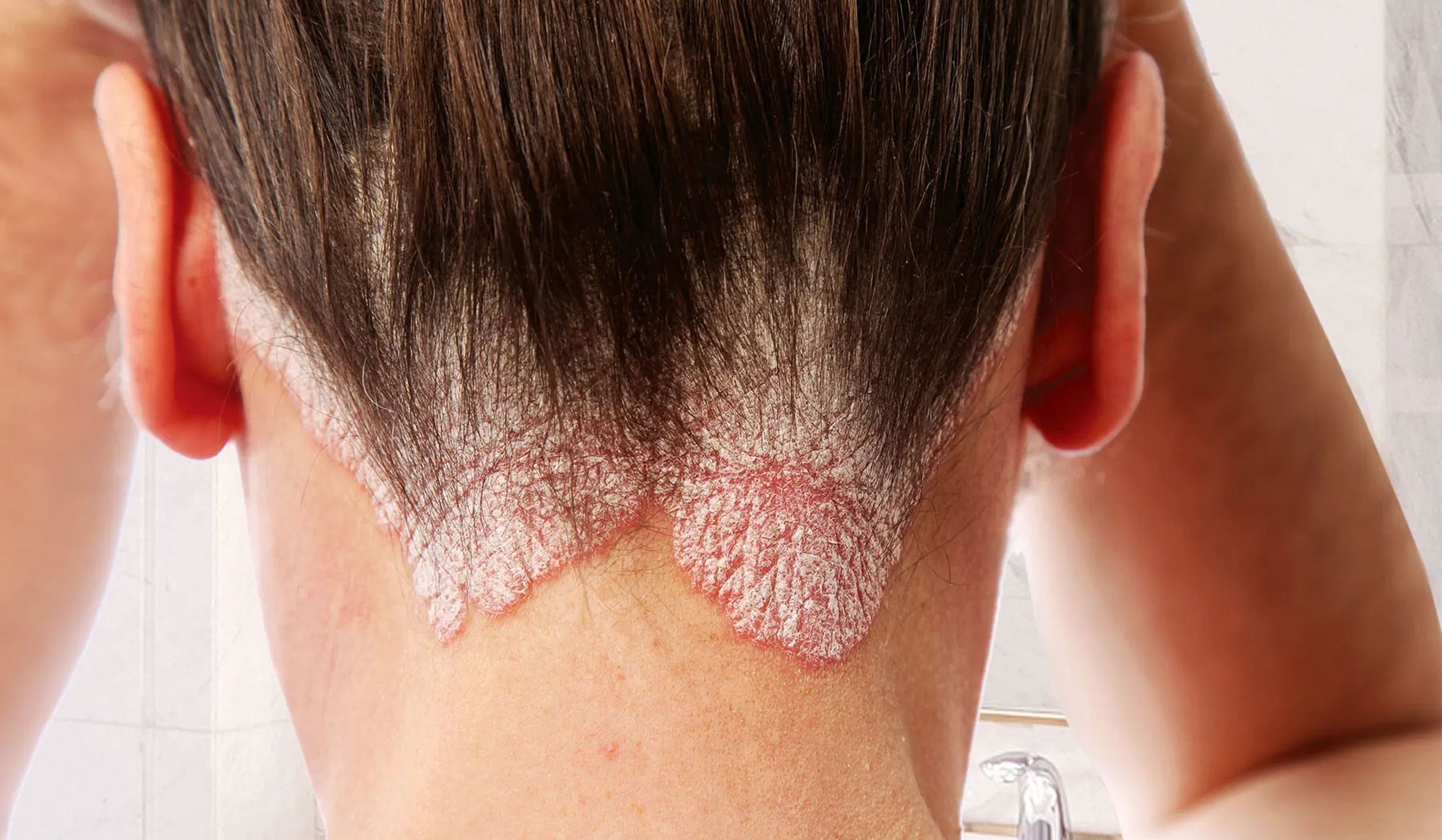
3. Scalp Dermatitis (Seborrheic Dermatitis)
- What it is: Chronic inflammatory condition of the scalp often related to yeast overgrowth.
- Symptoms: Itchy, flaky scalp with redness or greasy patches.
- Treatment:
- Medicated shampoos (zinc pyrithione, ketoconazole)
- Topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors
- Scalp hygiene education
4. Hair Breakage & Fragility
- Causes: Excessive heat styling, chemical treatments, nutritional deficiencies, underlying conditions.
- Symptoms: Short broken hairs, frizz, poor hair texture, split ends.
- Management:
- Hair shaft repair serums
- Oral nutritional supplements (Biotin, Iron, Vitamin D)
- Gentle hair care routine guidance
Diagnostic Tools
- Trichoscopy: A non-invasive dermatoscope-based imaging to examine hair roots, scalp condition, and follicle patterns.
- Pull Test & Wash Test: To evaluate active shedding.
- Blood Tests: To assess hormones, iron levels, thyroid function, and vitamin deficiencies.
Treatment Options
| Condition | First-line Treatment | Advanced/Adjunct Management |
|---|---|---|
| Alopecia Areata | Steroid injections | PRP, topical immunotherapy |
| Androgenetic Alopecia | Minoxidil, finasteride | PRP, microneedling, hair transplant |
| Scalp Dermatitis | Medicated shampoos | Topical antifungals/steroids |
| Hair Breakage | Hair care correction, supplements | Topical repair treatments, diet changes |
Pros & Cons of Treatments
| Treatment Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| PRP Therapy | Natural, stimulates growth, minimal downtime | Requires multiple sessions, mild discomfort |
| Minoxidil | Widely effective, easy application | Must be continued long-term, scalp irritation possible |
| Steroid Injections | Rapid regrowth in alopecia areata | Local discomfort, thinning with repeated use |
| Hair Transplant | Permanent, natural appearance | Surgical procedure, expensive, downtime involved |
| Medicated Shampoos | Control dandruff, non-invasive | Ongoing use may be needed |
| Oral Medications | Convenient and systemic effect | Hormonal side effects (e.g., in finasteride) |
Patient Education & Support
- The root causes of your hair disorder
- Treatment expectations and timelines
- Nutritional and lifestyle adjustments
Clinical Dermatology
Autoimmune Skin Diseases
Conditions We Specialize In
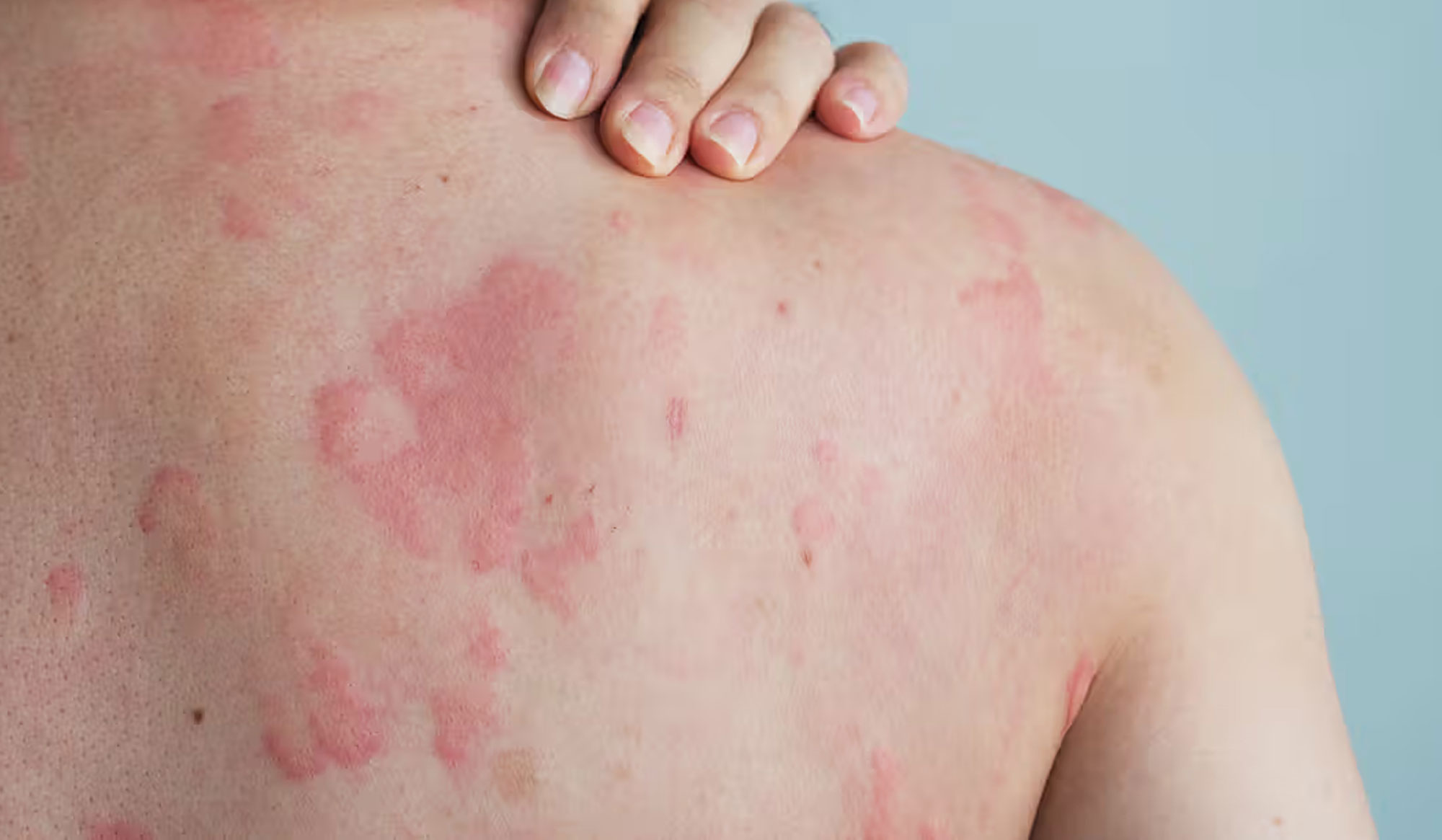
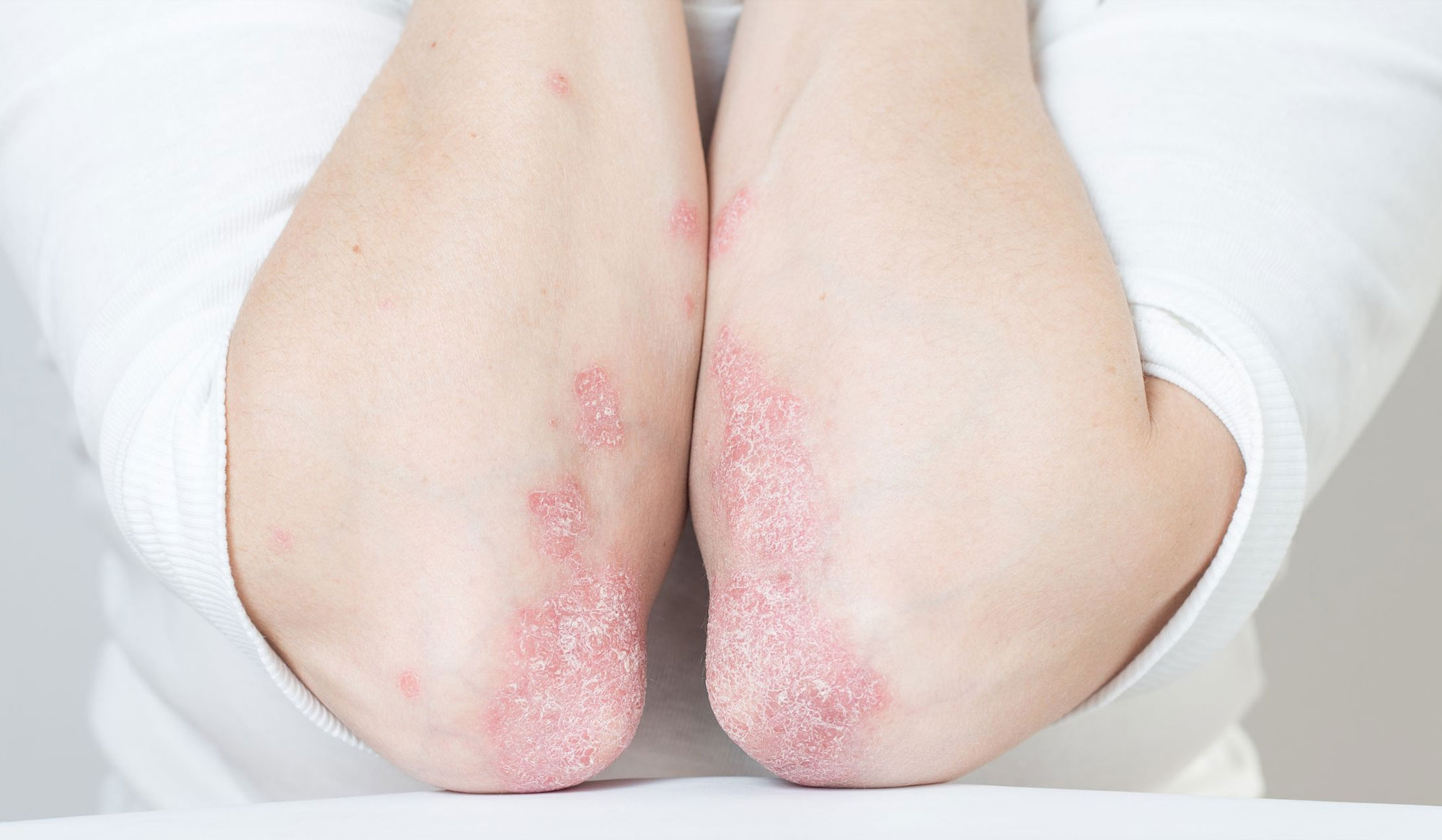
1. Psoriasis
- What it is: A chronic immune-mediated condition causing rapid skin cell turnover.
- Symptoms: Thick, red, scaly plaques on the elbows, knees, scalp, lower back; may involve joints (psoriatic arthritis).
- Types: Plaque psoriasis, guttate, inverse, pustular
- Management:
- Topical therapies (steroids, vitamin D analogs)
- Systemic drugs (methotrexate, cyclosporine)
- Biologics (Secukinumab, Adalimumab, Ustekinumab)
2. Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE)
- What it is: A cutaneous form of lupus causing persistent, inflamed skin lesions.
- Symptoms: Red or purple plaques with scarring, mostly on the face, scalp, and ears.
- Treatment:
- Topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors
- Antimalarial drugs (hydroxychloroquine)
- Sun protection is essential
3. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- What it is: A serious multisystem autoimmune disorder that also affects the skin.
- Skin Manifestations: Butterfly rash on cheeks, photosensitivity, vasculitis
- Diagnosis:
- ANA, dsDNA, complement levels, skin biopsy
- Treatment:
- Immunosuppressants (azathioprine, mycophenolate)
- Antimalarials
- Biologics (Belimumab)
4. Morphea (Localized Scleroderma)
- What it is: An autoimmune condition causing thick, hardened patches of skin.
- Symptoms: Ivory-colored plaques that may limit movement if deep
- Treatment:
- Topical steroids
- Phototherapy (UVA1)
- Systemic immunosuppressants for deep or progressive types
Diagnostic Tools
- Skin Biopsy: Confirms autoimmune activity and rules out infections or malignancies
- Blood Tests: ANA, ENA panel, inflammatory markers
- Imaging: For systemic involvement (in SLE/morphea)
- Phototesting: In cases of photosensitive eruptions
Treatment Protocols
| Condition | First-line Therapy | Advanced/Chronic Management |
|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis | Topical steroids, calcipotriol | Methotrexate, biologics |
| DLE | Topicals, sun protection | Hydroxychloroquine, steroids |
| SLE | Sunscreen, antimalarials | Immunosuppressants, biologics |
| Morphea | Steroids, moisturizers | Phototherapy, systemic immunomodulators |
Pros & Cons of Treatments
| Therapy Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Treatments | Safe for mild or localized cases | Limited effectiveness in widespread or deep disease |
| Systemic Drugs | Target disease activity throughout the body | Requires blood monitoring, risk of side effects |
| Biologics | Highly effective, targeted immune control | Expensive, possible immunosuppression risk |
| Phototherapy | Non-invasive, helpful in early morphea/psoriasis | Time-intensive, access may be limited |
Patient Education & Monitoring
- Track disease activity over time
- Monitor for systemic involvement
- Adjust therapy based on response
- Educate on trigger avoidance (e.g., sun exposure, stress, infections)
Clinical Dermatology
Sexually Transmitted Dermatoses
Conditions We Treat
1. Genital Herpes (Herpes Simplex Virus - HSV)
- What it is: A viral infection caused by HSV-1 or HSV-2, transmitted through intimate contact.
- Symptoms: Painful blisters, sores, burning, tingling sensation; may recur periodically.
- Diagnosis:
- Clinical examination
- Tzanck smear or PCR test
- Blood tests for HSV antibodies
- Treatment:
- Oral antivirals (acyclovir, valacyclovir)
- Suppressive therapy for frequent outbreaks
- Counseling on transmission risk and partner protection
2. Syphilis
- What it is: A bacterial STI caused by Treponema pallidum, presenting in stages if untreated.
- Stages & Symptoms:
- Primary: Painless genital ulcer (chancre)
- Secondary: Rash on palms/soles, lymphadenopathy
- Latent/Tertiary: Organ damage, neurological signs (if not treated early)
- Diagnosis:
- VDRL, RPR, TPHA blood tests
- Dark-field microscopy of lesion (if applicable)
- Treatment:
- Benzathine penicillin G injection (single or multiple doses depending on stage)
- Partner testing and treatment
- Ongoing follow-up and VDRL monitoring
3. Genital Warts (Human Papillomavirus - HPV)
- What it is: A viral STI caused by low-risk HPV strains (e.g., 6, 11), leading to skin-colored growths.
- Symptoms: Small, painless warty lesions on genitals, anus, or surrounding areas; may be solitary or clustered.
- Treatment Options:
- Cryotherapy (freezing)
- Laser ablation
- Topical agents (imiquimod, podophyllin)
- HPV vaccination (preventive in eligible patients)
Diagnostic & Support Services
- Physical exam & dermoscopy
- PCR testing & blood investigations
- Partner screening & education
- Psychosexual counseling
- Safe sex guidance & vaccine counseling
Treatment Overview
| Condition | First-line Treatment | Additional/Supportive Care |
|---|---|---|
| Genital Herpes | Oral antivirals | Suppressive therapy, partner education |
| Syphilis | Penicillin injection | Blood test monitoring, partner testing |
| Genital Warts | Cryotherapy, topical agents | Laser treatment, HPV vaccination (prophylactic) |
Pros & Cons of Treatments
| Treatment Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Oral antivirals | Reduces symptoms, shortens outbreaks | Doesn’t eliminate virus; may need ongoing therapy |
| Cryotherapy | Quick wart removal | May require multiple sessions; local irritation |
| Laser therapy | Precise and effective for resistant warts | Costlier; risk of minor scarring |
| Penicillin injection | Curative for syphilis when given early | Injection site pain; allergic reactions in rare cases |
| Counseling & Education | Empowers patients, reduces transmission | Requires openness and follow-up |
Patient-Centered, Confidential Care
- Private consultations in a judgment-free environment
- Accurate, discreet diagnostic testing
- Clear, honest communication about risks and prevention
- Emotional and psychological support during treatment